The student loan debt crisis in the United States has reached alarming levels, impacting individuals and the economy as a whole. With total student loan debt exceeding $1.7 trillion as of 2021, many Americans find themselves trapped in a cycle of debt, hindering their financial well-being and limiting their economic potential. In this blog, we will explore the case for student loan forgiveness as a necessary solution to alleviate the burden of debt on individuals and promote economic prosperity.
Table of Content
I. The Student Loan Debt Crisis
The rise of student loan debt in recent years has had profound consequences for individuals and the economy. Consider these numbers: the average student loan debt for the class of 2020 was approximately $37,000, and nearly 45 million Americans are burdened with student loan debt.
Individually, student loan debt places significant financial strain on borrowers. Monthly loan payments can eat up a substantial portion of their income, leaving little room for savings, investments, and essential living expenses. It is not uncommon for graduates to delay major life milestones, such as purchasing a home or starting a family, due to their debt obligations.
The broader economic impact is also significant. A study by the National Association of Realtors estimated that for every $1,000 in student loan debt, homeownership rates drop by about 2%. This decline in homeownership has implications for the housing market, consumer spending, and overall economic growth.
| Data Point | Value |
|---|---|
| Total outstanding student loan debt | $1.7 trillion |
| Average student loan debt for a college graduate | $30,000 |
| Number of borrowers with student loan debt | 45 million |
| Most common student loan forgiveness programs | Public service loan forgiveness, teacher loan forgiveness, disability discharge |
| Potential effects of student loan forgiveness | Increased economic activity, reduced household debt, increased educational attainment |
Total Debt Balance and its Composition
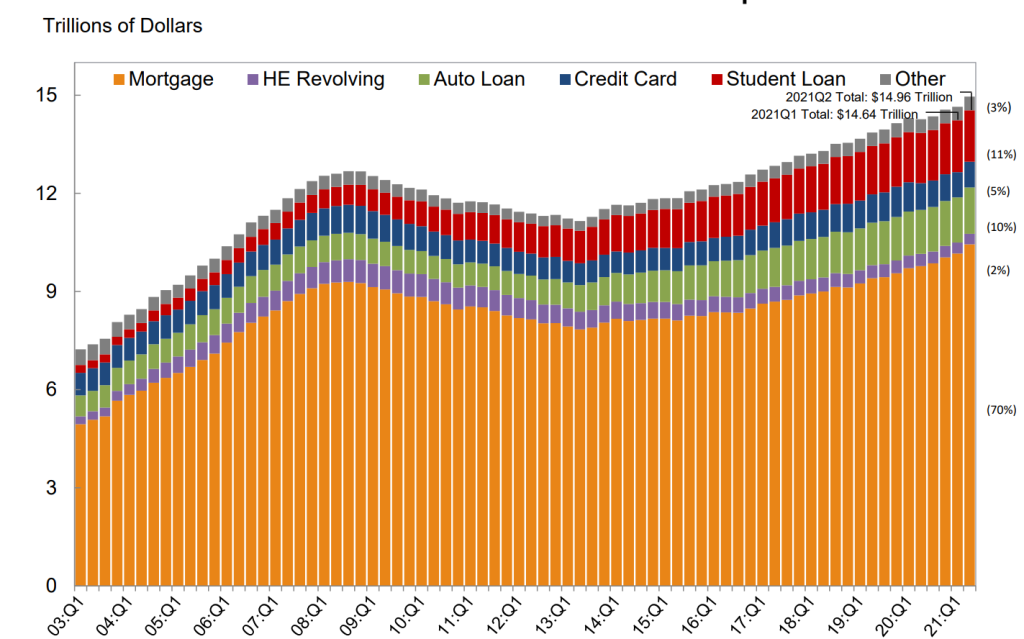
Number of Accounts by Loan Type
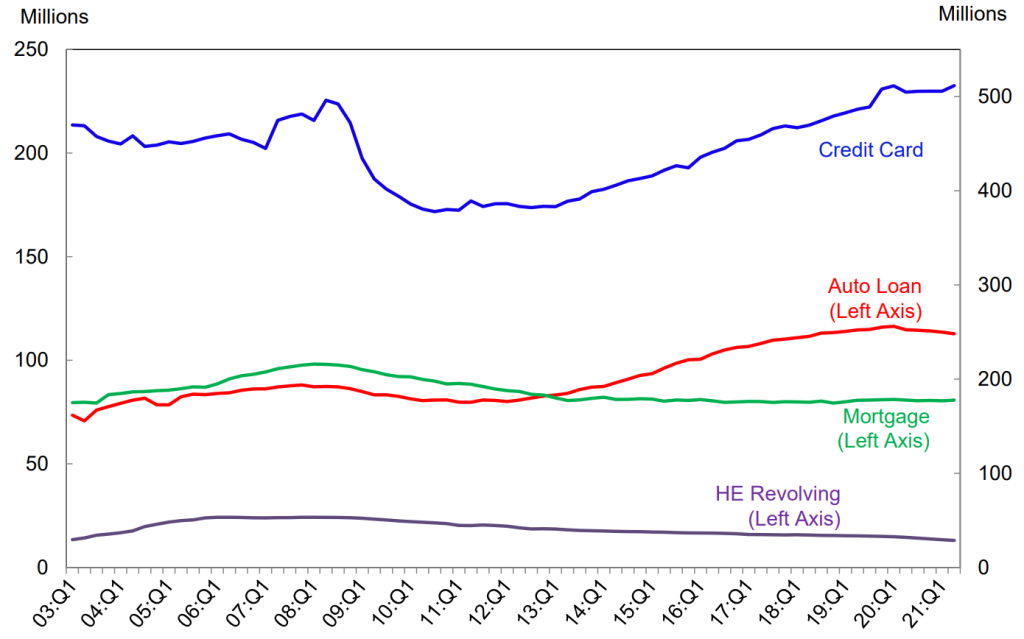
Mortgage Originations by Credit Score*
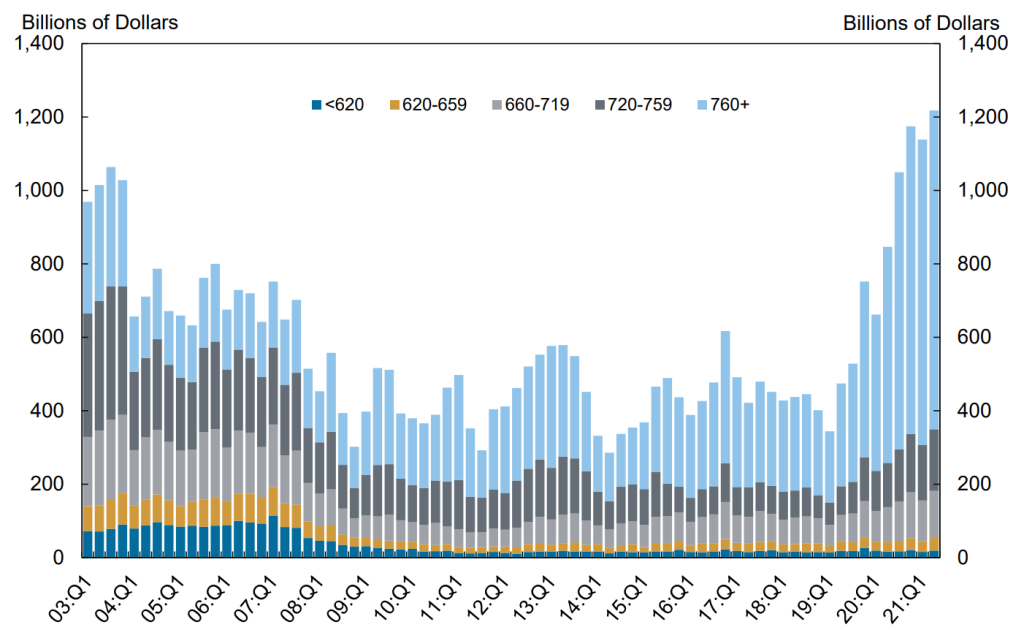
Total Debt Balance by Age
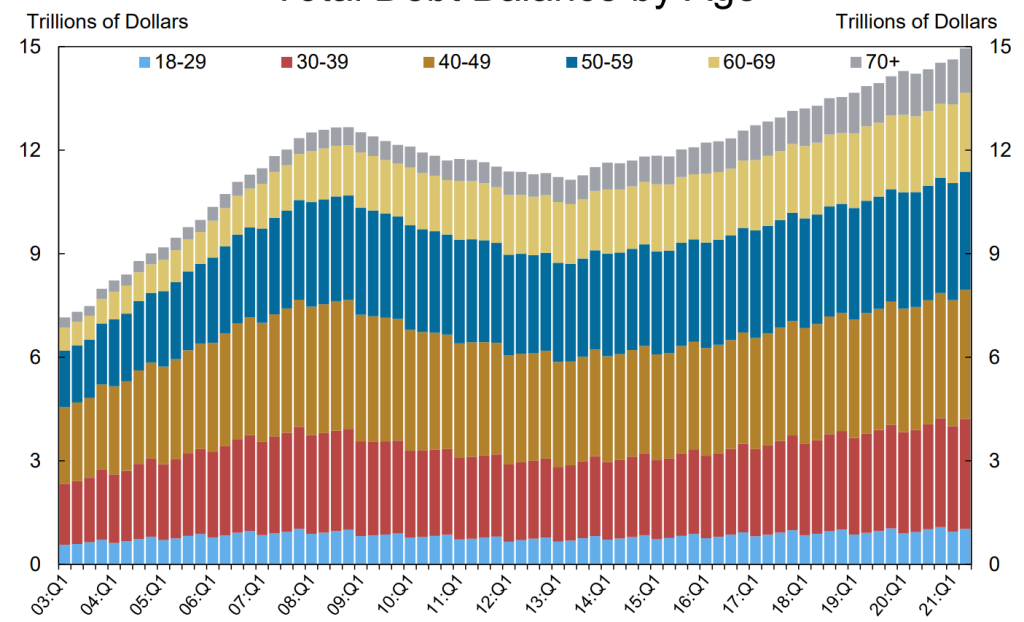
II. The Benefits of Student Loan Forgiveness
A. Individual Benefits
- Financial Relief: Student loan forgiveness offers immediate relief to borrowers, reducing financial stress and improving their quality of life. According to a study conducted by the American Psychological Association, high levels of student loan debt are associated with increased levels of stress, anxiety, and depression. By alleviating this burden, individuals can experience improved mental well-being and better financial stability.
- Increased Opportunities: Student loan forgiveness provides individuals with the freedom to pursue careers based on their passions and personal interests, rather than solely on financial considerations. For example, aspiring teachers may be more inclined to work in lower-paying school districts or underserved communities if they are not burdened by the weight of student loan debt.
- Boost to Credit Scores: Forgiving student loans can have a positive impact on credit scores, enabling borrowers to access other forms of credit, such as mortgages and business loans. This improved creditworthiness empowers individuals to make important financial decisions and participate more fully in the economy.
B. Economic Benefits
- Stimulating the Economy: By freeing up disposable income, student loan forgiveness injects money back into the economy. According to the Levy Economics Institute of Bard College, canceling all student debt would boost real GDP by $86 billion to $108 billion per year over a 10-year period. Increased consumer spending leads to job creation, business growth, and economic stimulus.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship: Student loan debt often deters individuals from pursuing entrepreneurial ventures due to the fear of financial failure. By providing debt relief, aspiring entrepreneurs can take calculated risks, innovate, and contribute to economic growth. A study by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia found that a 1% decrease in student loan debt is associated with a 0.4% increase in the likelihood of self-employment.
- Addressing Wealth Inequality: Student loan forgiveness helps redistribute resources, reducing the wealth gap and promoting social mobility. The burden of student loan debt disproportionately affects low-income individuals and communities of color. By providing relief, we can create a more equitable society and ensure that everyone has an equal opportunity to thrive.
C. Potential Effects of Student Loan Forgiveness
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased economic activity | Student loan forgiveness could free up borrowers to spend more money, which could boost the economy. This could lead to increased hiring and economic growth. |
| Reduced household debt | Student loan debt is a major source of household debt in the United States. Forgiveness could reduce this debt burden, which could make it easier for households to save and invest. |
| Increased educational attainment | Some people believe that student loan forgiveness would make it easier for people to afford college, which could lead to increased educational attainment. |
| Unfair to taxpayers | Some people believe that student loan forgiveness would be unfair to taxpayers who do not have student loan debt. They argue that taxpayers should not have to pay for the debts of others. |
III. Potential Challenges and Counterarguments
While student loan forgiveness offers significant benefits, it is essential to address potential challenges and counterarguments to ensure a sustainable and fair approach.
A. Moral Hazard
One concern often raised is the idea of incentivizing irresponsible borrowing behavior. However, studies have shown that the student loan debt crisis is primarily driven by the rising cost of education rather than irresponsible borrowing. To mitigate this concern, eligibility criteria can be implemented, focusing on borrowers who demonstrate financial need and responsible borrowing behavior. Additionally, promoting financial literacy programs can educate borrowers about responsible debt management and financial decision-making.
B. Cost and Funding
The cost of student loan forgiveness is a valid concern. However, it is important to consider the potential economic benefits and the long-term impact on the economy. Various funding sources can be explored to offset the expense, such as tax reforms, redirecting funds from other programs, and public-private partnerships. Careful consideration of the financial implications is essential to ensure a viable and sustainable solution.
C. Equity and Fairness
One argument against student loan forgiveness is the question of fairness for those who have already paid off their loans. Implementing a phased approach to forgiveness or providing targeted relief to low-income borrowers can address this concern. It is important to prioritize fairness and equity in any student loan forgiveness program.
D. Alternatives to Forgiveness
While student loan forgiveness is a comprehensive solution, alternatives should also be considered. Improving income-driven repayment plans to make them more effective and accessible can provide relief to borrowers. Furthermore, exploring the feasibility and potential benefits of tuition-free college can address the root cause of the student loan debt crisis.
IV. International Perspectives on Student Loan Forgiveness
Taking a look at international models can provide valuable insights into successful approaches to student loan forgiveness. Countries such as Sweden, Australia, and the United Kingdom have implemented various policies to alleviate student loan debt burdens. By examining these models, policymakers can gain insights into the potential benefits, challenges, and best practices for implementing student loan forgiveness programs.
V. Conclusion
The student loan debt crisis is a pressing issue that demands attention. Student loan forgiveness presents a viable solution to alleviate the burden on individuals and promote economic growth. By providing financial relief, expanding opportunities, and stimulating the economy, student loan forgiveness offers benefits to both borrowers and society as a whole. It is crucial for policymakers, educators, and citizens to prioritize finding sustainable solutions to address the student loan debt crisis and foster a brighter future for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about Student Loan Forgiveness
What is student loan forgiveness?
Student loan forgiveness is a program or initiative that allows borrowers to have a portion or all of their student loans forgiven, meaning they are no longer obligated to repay the forgiven amount. It provides financial relief to borrowers burdened by student loan debt.
What are the different types of student loan forgiveness programs?
There are various types of student loan forgiveness programs available. Some common ones include Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), Teacher Loan Forgiveness, Perkins Loan Cancellation, and Income-Driven Repayment Plan forgiveness options.
Who is eligible for student loan forgiveness?
Eligibility requirements for student loan forgiveness vary depending on the specific program. However, there are some general eligibility requirements that apply to most programs. These include:
- U.S. citizen or permanent resident: You must be a U.S. citizen or permanent resident to be eligible for most student loan forgiveness programs.
- Direct federal loans: Most student loan forgiveness programs only apply to direct federal loans. However, there are some exceptions, such as the Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program, which also applies to Federal Family Education Loans (FFELs).
- Employment: Some student loan forgiveness programs require you to be employed in a certain field or for a certain type of employer. For example, the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program requires you to work full-time for a qualifying public service employer.
- Payments: Some student loan forgiveness programs require you to make a certain number of qualifying payments before you can be eligible for forgiveness. For example, the PSLF Program requires you to make 120 qualifying payments.
In addition to these general eligibility requirements, some student loan forgiveness programs have additional requirements. For example, the Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program requires you to teach full-time for five consecutive years in a low-income school or educational service agency.
If you are interested in student loan forgiveness, it is important to carefully review the eligibility requirements for the specific program you are interested in. You can find more information about student loan forgiveness programs on the Federal Student Aid website.
Here are some of the most common student loan forgiveness programs and their eligibility requirements:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): This program forgives the remaining balance on your Direct Loans after you have made 120 qualifying payments while working full-time for a qualifying public service employer.
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness: This program forgives up to $17,500 of your Direct Loans after you have taught full-time for five consecutive years in a low-income school or educational service agency.
- Disability discharge: This program forgives the remaining balance on your Direct Loans if you are totally and permanently disabled.
- Borrower defense to repayment: This program allows you to have your loans discharged if you were misled or defrauded by your school.
- Closed school discharge: This program allows you to have your loans discharged if your school closed before you could complete your degree.
How do I apply for student loan forgiveness?
The application process for student loan forgiveness varies depending on the specific program. However, there are some general steps that you will need to follow:
- Check your eligibility: Before you apply for student loan forgiveness, you should carefully review the eligibility requirements for the specific program you are interested in. You can find more information about student loan forgiveness programs on the Federal Student Aid website.
- Gather your documentation: Once you have determined that you are eligible for student loan forgiveness, you will need to gather your documentation. This documentation will vary depending on the specific program you are applying for, but it may include things like your employment verification, your loan servicer information, and your tax returns.
- Complete the application: Once you have gathered your documentation, you will need to complete the application for student loan forgiveness. The application process for each program is different, so you will need to follow the instructions specific to the program you are applying for.
- Submit your application: Once you have completed the application, you will need to submit it to your loan servicer. Your loan servicer will then review your application and determine if you are eligible for forgiveness.
If you are approved for student loan forgiveness, your loan servicer will notify you and they will forgive the remaining balance on your loan.
Here are some additional tips for applying for student loan forgiveness:
- Start early: The application process for student loan forgiveness can be long and complex, so it is important to start early.
- Be organized: Keep track of your documentation and make sure that you have everything you need to complete the application.
- Be patient: The application process can take several months, so be patient and don’t give up.
What are the benefits of student loan forgiveness?
Student loan forgiveness offers several benefits. It provides borrowers with financial relief, freeing them from the burden of debt. It can improve mental well-being and quality of life, allowing individuals to pursue career paths based on passion rather than solely on financial considerations. Additionally, it can stimulate the economy through increased consumer spending and promote social mobility by reducing wealth inequality.
What are the drawbacks of student loan forgiveness?
While student loan forgiveness has numerous advantages, there are some drawbacks to consider. Critics argue that it may create moral hazard, potentially incentivizing irresponsible borrowing behavior. There are also concerns about the cost and funding of forgiveness programs and the potential impact on taxpayers.
What is the cost of student loan forgiveness?
The cost of student loan forgiveness depends on the specific program and the number of borrowers who are eligible. However, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) has estimated that the cost of forgiving all student loan debt would be about $1.6 trillion over the next decade.
Here are some of the factors that would affect the cost of student loan forgiveness:
- The amount of debt forgiven: The cost of student loan forgiveness would obviously be higher if the amount of debt forgiven was larger.
- The number of borrowers eligible: The cost of student loan forgiveness would also be higher if the number of borrowers eligible was larger.
- The repayment terms: The cost of student loan forgiveness would also be affected by the repayment terms of the loans. For example, if borrowers were required to make payments for a certain number of years before they were eligible for forgiveness, the cost of forgiveness would be lower.
It is important to note that the cost of student loan forgiveness is a matter of debate. Some people believe that the cost is too high and that it would be unfair to taxpayers who do not have student loan debt. Others believe that the cost is worth it, as it would free up borrowers to spend more money and boost the economy.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to forgive student loan debt is a political one. However, it is important to be aware of the potential costs of forgiveness before making a decision.
Who pays for student loan forgiveness?
The entity that pays for student loan forgiveness depends on the specific program. However, in most cases, the cost of student loan forgiveness is ultimately borne by taxpayers.
Here are some of the ways that taxpayers can pay for student loan forgiveness:
- Direct appropriation: The government can directly appropriate funds to pay for student loan forgiveness. This is the most common way that student loan forgiveness is funded.
- Increased taxes: The government can increase taxes to pay for student loan forgiveness. This is less common, but it is a possibility.
- Borrowers: In some cases, borrowers may be required to pay for their own student loan forgiveness. This is typically done through a “repayment premium” that is added to the borrower’s monthly payments.
It is important to note that the way that student loan forgiveness is funded is a matter of debate. Some people believe that the cost should be borne by taxpayers, while others believe that borrowers should be responsible for paying for their own forgiveness.
What is the future of student loan forgiveness?
The future of student loan forgiveness is uncertain. There is a lot of debate about whether or not student loan forgiveness is a good idea, and there is no clear consensus. However, there are a few things that we can say about the future of student loan forgiveness:
- The cost of student loan debt is rising. The total amount of student loan debt in the United States is over $1.7 trillion, and it is expected to continue to rise in the coming years. This rising cost of student loan debt is putting a strain on borrowers and the economy as a whole.
- There is growing support for student loan forgiveness. There is a growing movement in support of student loan forgiveness, and many people believe that it is a necessary step to address the rising cost of student loan debt. This support is coming from both Democrats and Republicans, and it is likely to continue to grow in the coming years.
- The Biden administration has taken some steps towards student loan forgiveness. The Biden administration has taken some steps towards student loan forgiveness, including extending the pause on student loan payments and expanding the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program. However, it is unclear whether or not the Biden administration will support broader student loan forgiveness.
Here are some of the potential scenarios for the future of student loan forgiveness:
- No student loan forgiveness: The government may decide not to forgive any student loan debt. This would be the status quo, and it would mean that borrowers would continue to be responsible for repaying their loans.
- Limited student loan forgiveness: The government may decide to forgive a limited amount of student loan debt. This could be done through a program like the PSLF, or it could be done through a one-time forgiveness program.
- Broad student loan forgiveness: The government may decide to forgive a significant amount of student loan debt. This could be done through a program that forgives all student loan debt, or it could be done through a program that forgives student loan debt for certain borrowers, such as those who work in public service.
It is impossible to say for sure what the future of student loan forgiveness will be. However, the rising cost of student loan debt and the growing support for forgiveness suggest that it is a topic that is likely to continue to be debated in the coming years.
What are the pros and cons of student loan forgiveness?
Pros of student loan forgiveness
- Reduced financial burden: Student loan forgiveness would reduce the financial burden on borrowers, freeing up money that could be used for other purposes, such as buying a home, starting a business, or saving for retirement.
- Increased economic activity: Student loan forgiveness could boost the economy by freeing up borrowers to spend more money. This could lead to increased hiring and economic growth.
- Improved educational attainment: Student loan forgiveness could make it easier for people to afford college, which could lead to increased educational attainment. This could benefit society as a whole by creating a more educated workforce.
Cons of student loan forgiveness
- Cost: Student loan forgiveness would be expensive, costing taxpayers billions of dollars.
- Fairness: Some people argue that student loan forgiveness would be unfair to taxpayers who do not have student loan debt.
- Incentives: Some people argue that student loan forgiveness would create perverse incentives, encouraging people to take out more student loans in the future.
What are the arguments for student loan forgiveness?
Proponents of student loan forgiveness argue that it helps alleviate the burden of debt, allows borrowers to pursue higher-paying careers, stimulates economic growth through increased consumer spending, and addresses wealth inequality by promoting social mobility.
What are the arguments against student loan forgiveness?
Opponents of student loan forgiveness raise concerns about the potential cost to taxpayers, the moral hazard of rewarding irresponsible borrowing behavior, and the fairness for individuals who have already repaid their loans. They may suggest alternative solutions or modifications to the existing programs.
What is the political climate surrounding student loan forgiveness?
The political climate surrounding student loan forgiveness varies and is subject to differing opinions and priorities among policymakers. It has become a significant topic of discussion and debate, with various proposals and potential reforms being considered.
What are the latest updates on student loan forgiveness?
- The Biden administration has extended the pause on student loan payments until August 31, 2023. This means that borrowers will not have to make payments on their student loans until August 31, 2023.
- The Biden administration has also expanded the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program. This means that more borrowers will be eligible for forgiveness under the PSLF program.
- The Biden administration is considering broader student loan forgiveness. However, it is unclear what form this forgiveness would take or when it would be implemented.
In addition to these updates, there are a number of other developments related to student loan forgiveness that are worth noting:
- A group of borrowers have filed a lawsuit against the Biden administration, arguing that the administration has the authority to forgive student loan debt under the Higher Education Act. The outcome of this lawsuit could have a significant impact on the future of student loan forgiveness.
- A number of Democratic lawmakers have introduced legislation that would forgive student loan debt. However, it is unclear whether or not this legislation will be passed by Congress.
The future of student loan forgiveness is uncertain, but the latest updates suggest that the Biden administration is taking steps to address the issue. It is important to stay up-to-date on the latest developments so that you can make informed decisions about your student loan debt.
What resources are available to help me learn more about student loan forgiveness?
There are several resources available to learn more about student loan forgiveness. Reputable websites like the U.S. Department of Education, Federal Student Aid, and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau provide information on various forgiveness programs and eligibility requirements. Additionally, consulting with a student loan counselor or financial advisor can offer personalized guidance based on your specific situation.
References:
- Federal Reserve Bank of New York. (2021). Quarterly Report on Household Debt and Credit: Q2 2021. https://www.newyorkfed.org/medialibrary/interactives/householdcredit/data/pdf/HHDC_2021Q2.pdf
- National Association of Realtors. (2021). Student Loan Debt and Housing Report. https://www.nar.realtor/sites/default/files/documents/2021-student-loan-debt-and-housing-report-11-17-2021.pdf
- American Psychological Association. (2014). Stress in America: Paying With Our Health. https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2014/stress-report.pdf
- Levy Economics Institute of Bard College. (2018). The Macroeconomic Effects of Student Debt Cancellation. http://www.levyinstitute.org/pubs/rpr_10_18.pdf
- Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia. (2018). Student Loan Debt and Entrepreneurship: Evidence from a Natural Experiment. https://www.philadelphiafed.org/-/media/research-and-data/publications/working-papers/2018/wp18-47.pdf
